GIS Data Types and Structures
GIS Data Types and Structures
Advantages and Disadvantages of Raster and Vector Data Models
| Feature | Raster Data Model | Vector Data Model |
|---|---|---|
| Precision in Graphics | ❌ Lower precision | ✅ Higher precision |
| Traditional Cartography | ❌ Less suited | ✅ Well suited |
| Data Volume | ❌ Larger | ✅ Smaller |
| Topology | ❌ Not inherently supported | ✅ Inherently supported |
| Computation | ✅ Faster for certain operations | ❌ Slower for certain operations |
| Update | ❌ More difficult | ✅ Easier |
| Continuous Space | ✅ Well suited | ❌ Less suited |
| Integration | ✅ Easier with remote sensing data | ❌ More complex |
| Discontinuous | ❌ Less suited | ✅ Well suited |
1. Vector and Feature Data
- Categorical and multivariate data types
- Contains attribute tables with additional information:
- Area measurements
- Length of shapes
- Geographic information (state, country)
Vector Data Types
- Points
- Dimensionless
- Represents single locations
- Lines
- One-dimensional
- Contains attribute records
- Polygons
- Two-dimensional
- Contains attribute records
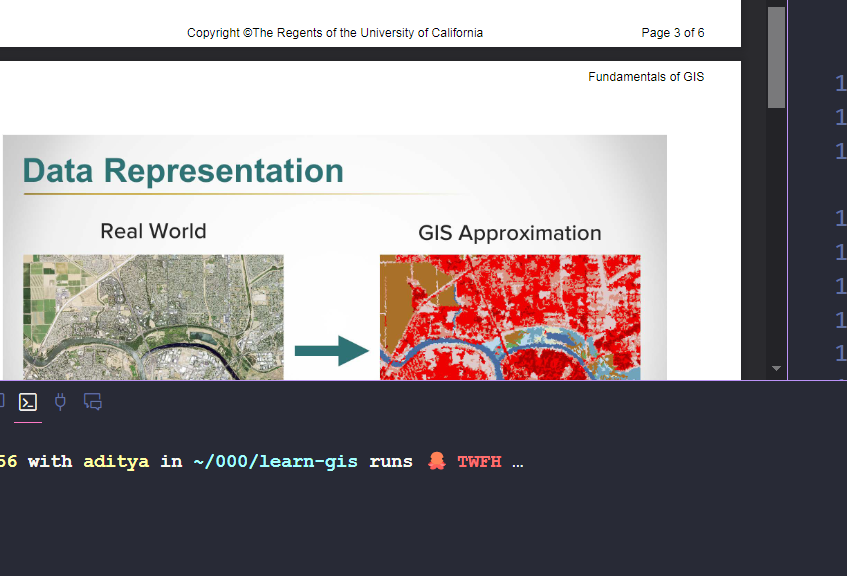
2. Raster Data
- Used for continuous surfaces
- Similar to image-based data
- Characteristics:
- Made up of fixed-size pixels
- Each pixel contains area information
- Contains various data types:
- RGB imagery
- Elevation data
- Surface information
- Attributes are per value, not per pixel
3. Spatial Data Containers
- File geodatabases
- SQLite/SpatiaLite databases
- GeoJSON
- PostGIS
Shapefiles (ESRI Format)
- Industry standard format
- Contains multiple files (up to 37)
- Uses dBase4 for data tables
- Limitations:
- Slower processing
- Larger size
- Being replaced by newer formats like GeoJSON
4. Map Documents
- Workspace for viewing and analyzing data
- Characteristics:
- Stores data representation
- Non-destructive editing
- Enables geoprocessing
- References data on disk
- Uses layers that:
- Stack and overlay
- Similar to image editing software layers
- Represent geographic data